结构化输出
¥Structured outputs
概述
¥Overview
为了在聊天会话中实现更长期的持久化,你可以将支持聊天内存类(如 )的默认内存 替换为。但是,在某些情况下,我们需要模型以结构化格式输出。例如,我们可能希望将模型输出存储在数据库中,并确保输出符合数据库模式。这种需求催生了结构化输出的概念,可以指示模型以特定的输出结构进行响应。
¥For many applications, such as chatbots, models need to respond to users directly in natural language. However, there are scenarios where we need models to output in a structured format. For example, we might want to store the model output in a database and ensure that the output conforms to the database schema. This need motivates the concept of structured output, where models can be instructed to respond with a particular output structure.
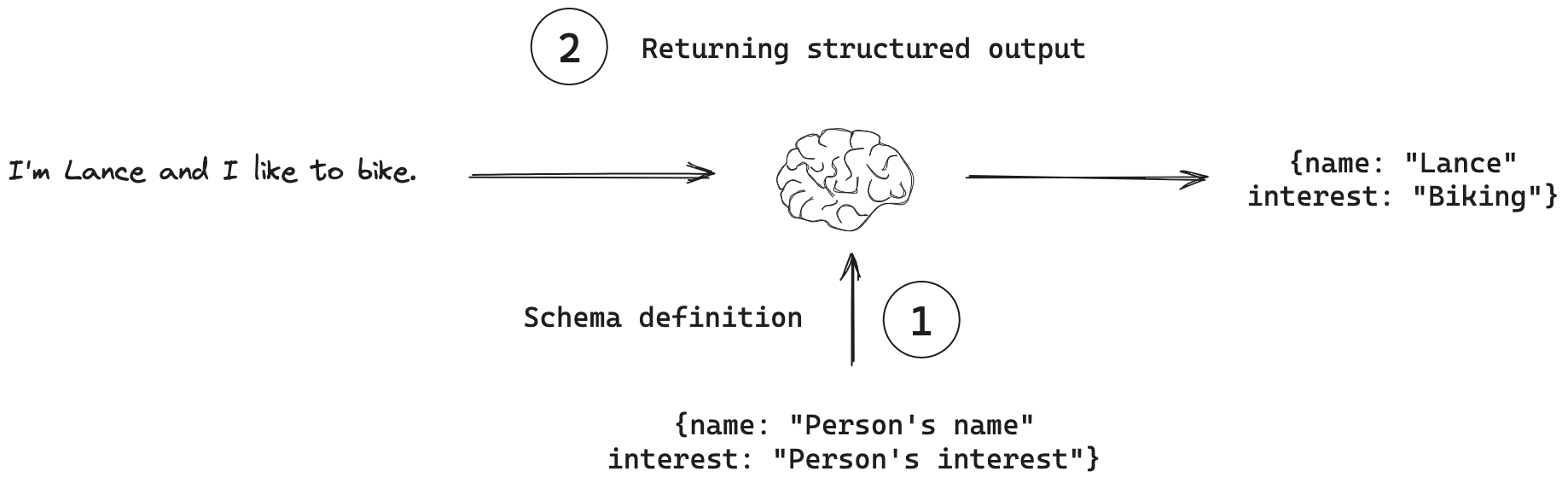
关键概念
¥Key concepts
(1)模式定义:输出结构表示为模式,可以通过多种方式定义。(2)返回结构化输出:模型被赋予此模式,并被指示返回符合该模式的输出。
¥(1) Schema definition: The output structure is represented as a schema, which can be defined in several ways. (2) Returning structured output: The model is given this schema, and is instructed to return output that conforms to it.
推荐使用
¥Recommended usage
此伪代码演示了使用结构化输出时的推荐工作流程。LangChain 提供了一种方法 withStructuredOutput(),可以自动执行将模式绑定到 model 并解析输出的过程。此辅助函数适用于所有支持结构化输出的模型提供程序。
¥This pseudo-code illustrates the recommended workflow when using structured output.
LangChain provides a method, withStructuredOutput(), that automates the process of binding the schema to the model and parsing the output.
This helper function is available for all model providers that support structured output.
// Define schema
const schema = { foo: "bar" };
// Bind schema to model
const modelWithStructure = model.withStructuredOutput(schema);
// Invoke the model to produce structured output that matches the schema
const structuredOutput = await modelWithStructure.invoke(userInput);
Schema 定义
¥Schema definition
核心概念是模型响应的输出结构需要以某种方式表示。虽然你可以使用的对象类型取决于你正在使用的模型,但在 TypeScript 中,通常允许或推荐使用一些常见的对象类型进行结构化输出。
¥The central concept is that the output structure of model responses needs to be represented in some way. While types of objects you can use depend on the model you're working with, there are common types of objects that are typically allowed or recommended for structured output in TypeScript.
结构化输出最简单、最常见的格式是 Zod 架构定义:
¥The simplest and most common format for structured output is a Zod schema definition:
import { z } from "zod";
const ResponseFormatter = z.object({
answer: z.string().describe("The answer to the user's question"),
followup_question: z
.string()
.describe("A followup question the user could ask"),
});
你还可以定义一个 JSONSchema 对象,Zod 模式在发送给模型提供程序之前会在内部转换为该对象:
¥You can also define a JSONSchema object, which is what Zod schemas are converted to internally before being sent to the model provider:
{
"$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema",
"$id": "https://example.com/product.schema.json",
"title": "ResponseFormatter",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"answer": {
"description": "The answer to the user's question",
"type": "string"
},
"followup_question": {
"description": "A followup question the user could ask",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": ["answer", "followup_question"]
}
返回结构化输出
¥Returning structured output
定义了模式后,我们需要一种方法来指示模型使用它。虽然一种方法是将此模式包含在提示中,并礼貌地请求模型使用它,但不建议这样做。提供了几种更强大的方法,它们利用了模型提供程序 API 中的原生功能。
¥With a schema defined, we need a way to instruct the model to use it. While one approach is to include this schema in the prompt and ask nicely for the model to use it, this is not recommended. Several more powerful methods that utilizes native features in the model provider's API are available.
使用工具调用
¥Using tool calling
许多 模型提供程序支持 工具调用,这个概念在我们的 工具调用指南 中进行了更详细的讨论。简而言之,工具调用涉及将工具绑定到模型,并且在适当的情况下,模型可以决定调用此工具并确保其响应符合工具的模式。考虑到这一点,核心概念很简单:使用我们的模式创建一个工具并将其绑定到模型!下面是一个使用上面定义的 ResponseFormatter 模式的示例:
¥Many model providers support tool calling, a concept discussed in more detail in our tool calling guide.
In short, tool calling involves binding a tool to a model and, when appropriate, the model can decide to call this tool and ensure its response conforms to the tool's schema.
With this in mind, the central concept is straightforward: create a tool with our schema and bind it to the model!
Here is an example using the ResponseFormatter schema defined above:
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: "gpt-4",
temperature: 0,
});
// Create a tool with ResponseFormatter as its schema.
const responseFormatterTool = tool(async () => {}, {
name: "responseFormatter",
schema: ResponseFormatter,
});
// Bind the created tool to the model
const modelWithTools = model.bindTools([responseFormatterTool]);
// Invoke the model
const aiMsg = await modelWithTools.invoke(
"What is the powerhouse of the cell?"
);
JSON 模式
¥JSON mode
除了工具调用之外,一些模型提供程序还支持名为 JSON mode 的功能。这支持 JSON 模式定义作为输入,并强制模型生成符合要求的 JSON 输出。你可以找到支持 JSON 模式 此处 的模型提供程序表。下面是一个如何在 OpenAI 中使用 JSON 模式的示例:
¥In addition to tool calling, some model providers support a feature called JSON mode.
This supports JSON schema definition as input and enforces the model to produce a conforming JSON output.
You can find a table of model providers that support JSON mode here.
Here is an example of how to use JSON mode with OpenAI:
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4",
}).bind({
response_format: { type: "json_object" },
});
const aiMsg = await model.invoke(
"Return a JSON object with key 'random_nums' and a value of 10 random numbers in [0-99]"
);
console.log(aiMsg.content);
// Output: {
// "random_nums": [23, 47, 89, 15, 34, 76, 58, 3, 62, 91]
// }
需要注意的一点:模型仍然返回一个字符串,需要将其解析为 JSON 对象。当然,如果你需要更高级的功能,可以简单地使用 json 库或 JSON 输出解析器。有关更多详细信息,请参阅此 JSON 输出解析器操作指南。
¥One important point to flag: the model still returns a string, which needs to be parsed into a JSON object.
This can, of course, simply use the json library or a JSON output parser if you need more advanced functionality.
See this how-to guide on the JSON output parser for more details.
import json
const jsonObject = JSON.parse(aiMsg.content)
// {'random_ints': [23, 47, 89, 15, 34, 76, 58, 3, 62, 91]}
结构化输出方法
¥Structured output method
使用上述方法生成结构化输出时存在一些挑战:
¥There are a few challenges when producing structured output with the above methods:
(1)如果使用工具调用,则需要将工具调用参数从对象解析回原始模式。
¥(1) If using tool calling, tool call arguments needs to be parsed from an object back to the original schema.
(2)此外,当我们想要强制执行结构化输出时,需要指示模型始终使用该工具,这是提供程序特定的设置。
¥(2) In addition, the model needs to be instructed to always use the tool when we want to enforce structured output, which is a provider specific setting.
(3)如果使用 JSON 模式,则需要将输出解析为 JSON 对象。
¥(3) If using JSON mode, the output needs to be parsed into a JSON object.
考虑到这些挑战,LangChain 提供了一个辅助函数 (withStructuredOutput()) 来简化流程。
¥With these challenges in mind, LangChain provides a helper function (withStructuredOutput()) to streamline the process.
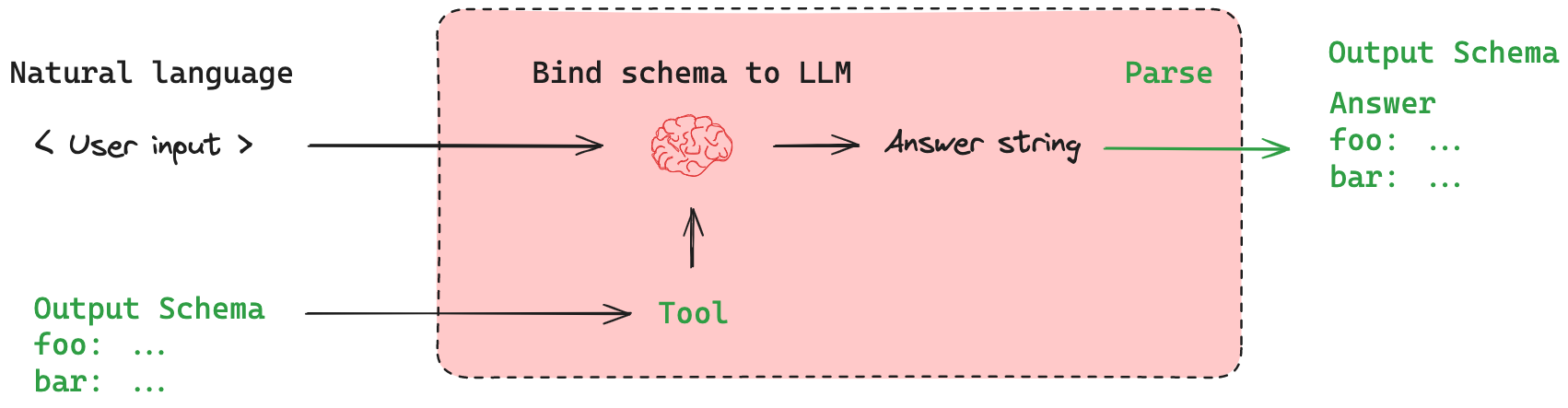
这既将模式绑定到模型作为工具,又将输出解析为指定的输出模式。
¥This both binds the schema to the model as a tool and parses the output to the specified output schema.
// Bind the schema to the model
const modelWithStructure = model.withStructuredOutput(ResponseFormatter);
// Invoke the model
const structuredOutput = await modelWithStructure.invoke(
"What is the powerhouse of the cell?"
);
// Get back the object
console.log(structuredOutput);
// { answer: "The powerhouse of the cell is the mitochondrion. Mitochondria are organelles that generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a source of chemical energy.", followup_question: "What is the function of ATP in the cell?" }
有关使用方法的更多详细信息,请参阅我们的 操作指南!
¥For more details on usage, see our how-to guide.