检索器
¥Retrievers
概述
¥Overview
存在许多不同类型的检索系统,包括向量存储、图形数据库和关系数据库。随着大型语言模型的普及,检索系统已成为 AI 应用(例如 RAG)的重要组成部分。由于检索系统的重要性和多样性,LangChain 提供了一个统一的接口,用于与不同类型的检索系统进行交互。LangChain retriever 接口简单易懂:
¥Many different types of retrieval systems exist, including vectorstores, graph databases, and relational databases. With the rise on popularity of large language models, retrieval systems have become an important component in AI application (e.g., RAG). Because of their importance and variability, LangChain provides a uniform interface for interacting with different types of retrieval systems. The LangChain retriever interface is straightforward:
输入:查询(字符串)
¥Input: A query (string)
输出:文档列表(标准化的 LangChain 文档 对象)
¥Output: A list of documents (standardized LangChain Document objects)
关键概念
¥Key concept
所有检索器都实现了一个简单的接口,用于使用自然语言查询检索文档。
¥All retrievers implement a simple interface for retrieving documents using natural language queries.
接口
¥Interface
对检索器的唯一要求是能够接受查询并返回文档。具体来说,LangChain 的检索器类 只需要实现 _getRelevantDocuments 方法,该方法接受 query: string 参数并返回与查询最相关的 文档 对象列表。获取相关文档的底层逻辑由检索器指定,可以是任何对应用最有用的逻辑。
¥The only requirement for a retriever is the ability to accepts a query and return documents.
In particular, LangChain's retriever class only requires that the _getRelevantDocuments method is implemented, which takes a query: string and returns a list of Document objects that are most relevant to the query.
The underlying logic used to get relevant documents is specified by the retriever and can be whatever is most useful for the application.
LangChain 检索器是一个 runnable,它是 LangChain 组件的标准接口。这意味着它有一些常用方法,包括 invoke,可用于与其交互。检索器可以通过查询调用:
¥A LangChain retriever is a runnable, which is a standard interface is for LangChain components.
This means that it has a few common methods, including invoke, that are used to interact with it. A retriever can be invoked with a query:
const docs = await retriever.invoke(query);
检索器返回一个 文档 对象列表,该对象具有两个属性:
¥Retrievers return a list of Document objects, which have two attributes:
pageContent:本文档的内容。当前为字符串。¥
pageContent: The content of this document. Currently is a string.metadata:与此文档关联的任意元数据(例如,文档 ID、文件名、来源等)。¥
metadata: Arbitrary metadata associated with this document (e.g., document id, file name, source, etc).
观看我们的 操作指南,了解如何构建你自己的自定义检索器。
¥See our how-to guide on building your own custom retriever.
常见类型
¥Common types
尽管检索器界面非常灵活,但一些常见的检索系统类型仍然经常被使用。
¥Despite the flexibility of the retriever interface, a few common types of retrieval systems are frequently used.
搜索 API
¥Search apis
需要注意的是,检索器不需要实际存储文档。例如,我们可以在搜索 API 之上构建检索器,仅返回搜索结果!
¥It's important to note that retrievers don't need to actually store documents. For example, we can be built retrievers on top of search APIs that simply return search results!
关系数据库或图数据库
¥Relational or graph database
检索器可以构建在关系数据库或图形数据库之上。在这些情况下,使用 查询分析 技术从自然语言构建结构化查询至关重要。例如,你可以使用文本到 SQL 的转换构建 SQL 数据库的检索器。这允许在后台将自然语言查询(字符串)检索器转换为 SQL 查询。
¥Retrievers can be built on top of relational or graph databases. In these cases, query analysis techniques to construct a structured query from natural language is critical. For example, you can build a retriever for a SQL database using text-to-SQL conversion. This allows a natural language query (string) retriever to be transformed into a SQL query behind the scenes.
词汇搜索
¥Lexical search
正如我们在 retrieval 概念回顾中所讨论的,许多搜索引擎都是基于将查询中的单词与每个文档中的单词进行匹配。BM25 和 TF-IDF 是 两种流行的词汇搜索算法。LangChain 拥有适用于多种流行词汇搜索算法/引擎的检索器。
¥As discussed in our conceptual review of retrieval, many search engines are based upon matching words in a query to the words in each document. BM25 and TF-IDF are two popular lexical search algorithms. LangChain has retrievers for many popular lexical search algorithms / engines.
向量存储
¥Vector store
向量存储 是一种强大而高效的非结构化数据索引和检索方法。可以通过调用 asRetriever() 方法将向量存储用作检索器。
¥Vector stores are a powerful and efficient way to index and retrieve unstructured data.
An vectorstore can be used as a retriever by calling the asRetriever() method.
const vectorstore = new MyVectorStore();
const retriever = vectorstore.asRetriever();
高级检索模式
¥Advanced retrieval patterns
集成
¥Ensemble
由于检索器接口非常简单,只需根据搜索查询返回一个 Document 对象列表,因此可以使用集成技术组合多个检索器。当你拥有多个擅长查找不同类型相关文档的检索器时,这一点尤其有用。创建一个结合多个检索器和线性加权分数的 集成检索器 很容易:
¥Because the retriever interface is so simple, returning a list of Document objects given a search query, it is possible to combine multiple retrievers using ensembling.
This is particularly useful when you have multiple retrievers that are good at finding different types of relevant documents.
It is easy to create an ensemble retriever that combines multiple retrievers with linear weighted scores:
// Initialize the ensemble retriever
const ensembleRetriever = new EnsembleRetriever({
retrievers: [bm25Retriever, vectorStoreRetriever],
weights: [0.5, 0.5],
});
在集成时,我们如何组合来自多个检索器的搜索结果?这催生了重新排序的概念,它获取多个检索器的输出,并使用更复杂的算法(例如 倒数排序融合 (RRF))将它们组合起来。
¥When ensembling, how do we combine search results from many retrievers? This motivates the concept of re-ranking, which takes the output of multiple retrievers and combines them using a more sophisticated algorithm such as Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF).
源文档保留
¥Source document retention
许多检索器利用某种索引使文档易于搜索。索引过程可以包括转换步骤(例如,向量存储通常使用文档拆分)。无论使用哪种转换,保留转换后的文档与原始文档之间的链接都非常有用,这使得检索器能够返回原始文档。
¥Many retrievers utilize some kind of index to make documents easily searchable. The process of indexing can include a transformation step (e.g., vectorstores often use document splitting). Whatever transformation is used, can be very useful to retain a link between the transformed document and the original, giving the retriever the ability to return the original document.
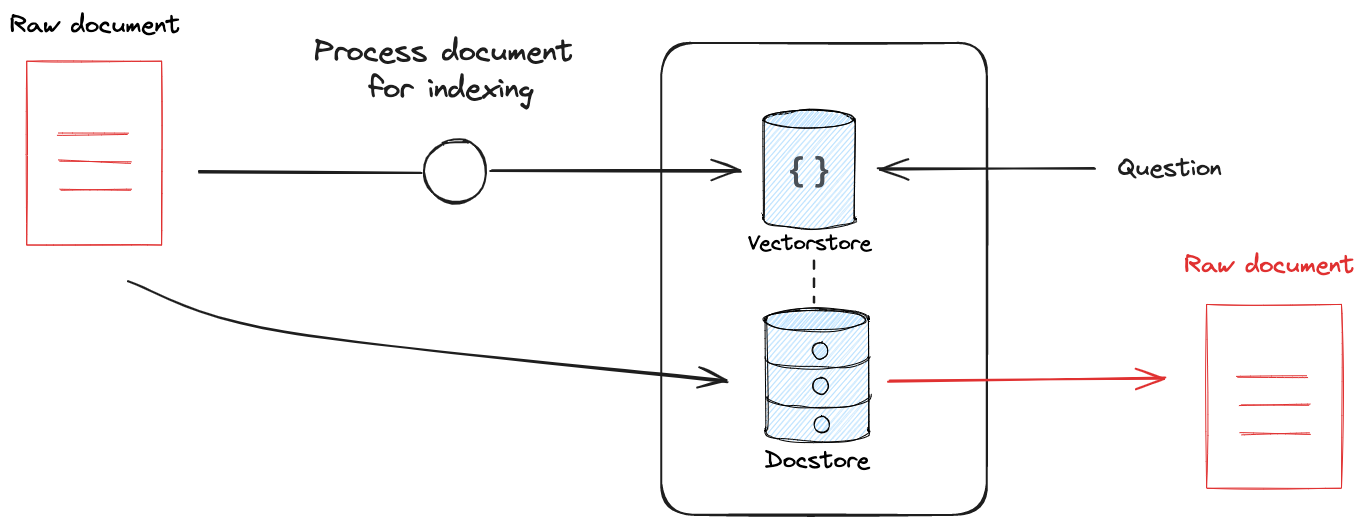
这在人工智能应用中尤其有用,因为它可以确保模型的文档上下文不会丢失。例如,你可以使用较小的块大小来索引向量存储中的文档。如果你仅返回块作为检索结果,则模型将丢失块的原始文档上下文。
¥This is particularly useful in AI applications, because it ensures no loss in document context for the model. For example, you may use small chunk size for indexing documents in a vectorstore. If you return only the chunks as the retrieval result, then the model will have lost the original document context for the chunks.
LangChain 有两种不同的检索器可用于应对这一挑战。多向量 检索器允许用户使用任何文档转换(例如,使用 LLM 编写文档摘要)进行索引,同时保留与源文档的链接。ParentDocument 检索器将来自文本分割器转换的文档块链接起来进行索引,同时保留与源文档的链接。
¥LangChain has two different retrievers that can be used to address this challenge. The Multi-Vector retriever allows the user to use any document transformation (e.g., use an LLM to write a summary of the document) for indexing while retaining linkage to the source document. The ParentDocument retriever links document chunks from a text-splitter transformation for indexing while retaining linkage to the source document.
| Name | Index Type | Uses an LLM | When to Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ParentDocument | Vector store + Document Store | No | If your pages have lots of smaller pieces of distinct information that are best indexed by themselves, but best retrieved all together. | This involves indexing multiple chunks for each document. Then you find the chunks that are most similar in embedding space, but you retrieve the whole parent document and return that (rather than individual chunks). |
| Multi Vector | Vector store + Document Store | Sometimes during indexing | If you are able to extract information from documents that you think is more relevant to index than the text itself. | This involves creating multiple vectors for each document. Each vector could be created in a myriad of ways - examples include summaries of the text and hypothetical questions. |
请参阅我们关于使用 ParentDocument 检索器的 操作指南。
¥See our how-to guide on using the ParentDocument retriever.
观看我们的 操作指南,了解如何使用多向量检索器。
¥See our how-to guide on using the MultiVector retriever.
观看我们关于 多向量检索器 的从 Scratch 构建 RAG 视频。
¥See our RAG from Scratch video on the multi vector retriever.